The Internet is getting faster, according to the latest quarterly State of the Internet report from Akamai Technologies. Global connection speed increased 14 percent year over year, and as the IPv4 addressing space was recently depleted in North America, analysts recommend accelerating IPv6 adoption in the U.S. — now at 18 percent — to keep up the pace with leading adopters like Belgium, a nation that sees 35 percent of its connections occurring over IPv6.
While some areas of the world saw minor declines in broadband adoption, the overall trend still points toward strong growth, said David Belson, senior director of industry and data intelligence at Akamai Technologies and the report’s editor.
“The investments that are being made in improving broadband and improving connectivity are in fact paying off. What we’re seeing also is increased Internet usage, and it shows also that it’s still obviously worth investing in improving broadband connectivity,” Belson said. “While things have improved over time, there’s still a long way to go, and in many cases there are geographies that are a lot further behind than others.”
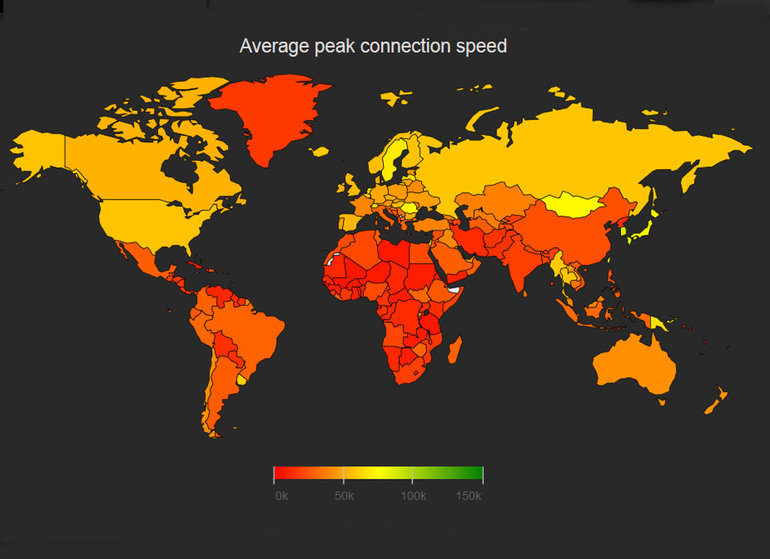
The report concludes that the globe’s average connection speed is 5.1 Mbps. South Korea maintains the highest average connection speed of any nation at 20.5 Mbps, despite an 11 percent quarter-over-quarter speed decrease and a 19 percent year-over-year decrease. Also in the top 10 are Sweden, Norway, Switzerland, Hong Kong, the Netherlands, Japan, Finland, Latvia and the Czech Republic. The report also contains other speed analysis like percentage of overall population with a connection over 4 Mbps (see map below) and peak connection speed.